Types As Well As Function Of White Blood Cells
Neutrophils deal with infection by destroying harmful bacteria and fungis that attack the body. Bone marrow is the squishy cells discovered in larger bones such as the pelvis, vertebrae, and ribs. It starts when the bone marrow begins to rapidly generate irregular white blood cells called leukemia cells. They might crowd out regular leukocyte, red cell, as well as platelets, making it hard for the regular cells to do their work.
For example, a high neutrophil count could mean a typical infection, a physical anxiety or cancer, whereas really high lymphocyte count would certainly indicate AIDS. A microbial infection is normally present when your eosinophil and monocyte matter is more than typical. A healthy adult human has in between 4,500 and also 11,000 leukocyte per cubic millimeter of blood.
Do low white blood cells make you tired?
Answer • Leukopenia is a low white blood cell https://raygarv52d.wixsite.com/eduardonpvr845/post/leukocyte-news-and-also-most-current-updates count. In itself, it doesn't usually produce fatigue. White blood cells are the body's Armed Forces, keeping infections from occurring. A low count can lead to repeated infections.
What Is Leukemia?
Normally, individuals create regarding 100 billion leukocyte a day. The variety of leukocyte in an offered volume of blood is revealed as cells per microliter of blood.
- The secretion of thyrotropin itself is mediated by thyrotropin-releasing hormonal agent secreted by the hypothalamus.
- All these functions are regulated by attachment of the active form of thyroid hormone T3 to particular members of the nuclear receptors family members.
- These particles have additionally critical functions in early mind advancement, somatic development, bone growth, protein synthesis as well as controling manufacturing of red blood cells.
- Hormone result from the thyroid is mediated by thyroid stimulating hormone produced by anterior pituitary.
Can thyroid affect white blood count?
Hyperthyroidism causes mild decreases in total white blood cell count, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and increases, normal or mild decreases in total white blood cell count. Generally it seems that hypothyroidism causes hypoplasia in all myeloid cell lineages and hyperthyroidism result in hyperplasia.
Leukocyte Disorders Treatment At Dana.
Hormone outcome from the thyroid is mediated by thyroid stimulating hormone produced by former pituitary. The secretion of thyrotropin itself is moderated by thyrotropin-releasing hormonal agent secreted by the hypothalamus.
Neutrophils.
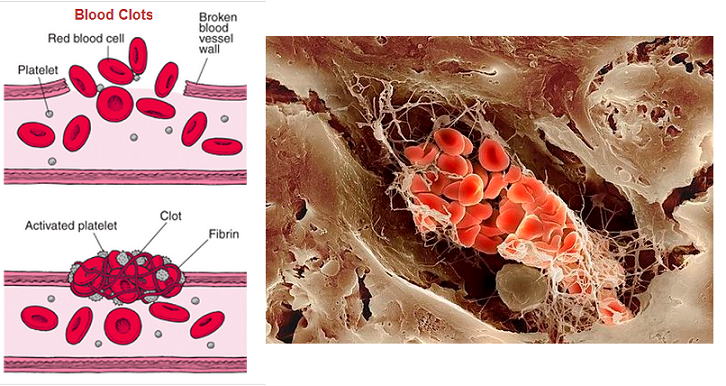
An individual with a low white blood cells matter is more prone to infections, since their body lacks sources for fighting microorganisms and infections. It can be triggered by a vitamin deficiency, or by something extra major such as leukemia or lymphoma. The number of leukocytes in the blood is frequently a sign of condition. There are generally in between 4 × 109 and 1.1 × 1010 leukocyte in a litre of blood, making up roughly 1% of blood in a healthy adult. A boost in the number of leukocytes over the ceilings is called leukocytosis, and also in leukopenia, this number is a lot less than the lower limitation.
